How To Find Missing Angles In A Triangle Using Trig : Step 3 calculate adjacent / hypotenuse = 6,750/8,100 = 0.8333.
How To Find Missing Angles In A Triangle Using Trig : Step 3 calculate adjacent / hypotenuse = 6,750/8,100 = 0.8333.. Let us name it y. Recall the three main trigonometric functions: Sides in geometry, if you're given a right triangle with missing angles or sides, you can use trigonometric ratios—sine, cosine, or tangent—to find them. How do you find the missing angles of a right triangle? The inverse ratios start with the ratio and then find the angle that produces this ratio.
E) what if we now wanted to find the measure of the other acute angle of the triangle? How to find the unknown angle? Label the side lengths, relative to the angle we're after, using a, o and h. Cos a° = 6,750/8,100 = 0.8333. Using the labels, made in step 1, look for the only one of the words soh, cah, or toa that contains both of the letters o and h, or a and h, or o and a.
Cos a° = 6,750/8,100 = 0.8333.
Adjacent, opposite and hypotenuse, in a right triangle is shown below. Using trig ratios to solve triangles: We certainly could use trigonometry again, but can you think of a faster way to find the value of y? Sides in geometry, if you're given a right triangle with missing angles or sides, you can use trigonometric ratios—sine, cosine, or tangent—to find them. Step 3 calculate adjacent / hypotenuse = 6,750/8,100 = 0.8333. Step by step guide to finding missing sides and angles of a right triangle by using sine, cosine or tangent, we can find an unknown side in a right triangle when we have one length, and one angle (apart from the right angle). Step 2 soh cah toa tells us we must use c osine. 1 10 cos 24.62 11 x =≈− ⎛⎞⎜⎟ ⎝⎠ d so 24.62x ≈ d. Given a right angle triangle, the method for finding an unknown angle a, can be summarized in three steps : Cos a° = 6,750/8,100 = 0.8333. Label the side lengths, relative to the angle we're after, using a, o and h. 👉 learn how to find a missing angle of a right triangle. E) what if we now wanted to find the measure of the other acute angle of the triangle?
Label the side lengths, relative to the angle we're after, using a, o and h. 🌎 brought to you by: How do you find the missing angles of a right triangle? Step by step guide to finding missing sides and angles of a right triangle by using sine, cosine or tangent, we can find an unknown side in a right triangle when we have one length, and one angle (apart from the right angle). Step 1 the two sides we know are a djacent (6,750) and h ypotenuse (8,100).
Step 1 the two sides we know are a djacent (6,750) and h ypotenuse (8,100).
Recall the three main trigonometric functions: Step 1 the two sides we know are a djacent (6,750) and h ypotenuse (8,100). 👉 learn how to find a missing angle of a right triangle. To help you decide which of the three trigonometric ratios to use, you can label the sides of the triangle as adjacent or opposite. Step 2 soh cah toa tells us we must use c osine. A right triangle is a triangle that has 90 degrees as one of its angles. Adjacent, opposite and hypotenuse, in a right triangle is shown below. Cos a° = 6,750/8,100 = 0.8333. Sides in geometry, if you're given a right triangle with missing angles or sides, you can use trigonometric ratios—sine, cosine, or tangent—to find them. How do you calculate the missing side of a triangle? Step 3 calculate adjacent / hypotenuse = 6,750/8,100 = 0.8333. 🌎 brought to you by: How to find the unknown angle?
They are sometimes also called the arcsin, arccos, and arctan. Find the size of angle a°. 🌎 brought to you by: How do you find the missing angles of a right triangle? Label the side lengths, relative to the angle we're after, using a, o and h.
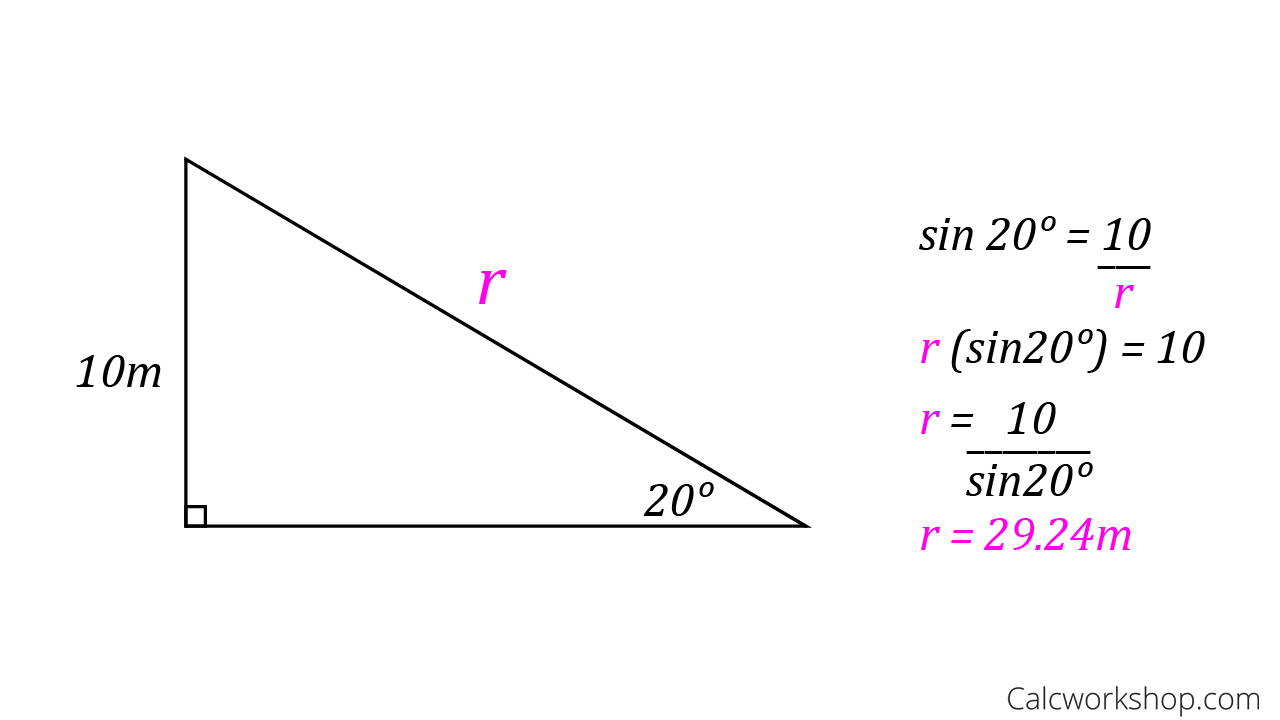
The inverse ratios start with the ratio and then find the angle that produces this ratio.
Using the labels, made in step 1, look for the only one of the words soh, cah, or toa that contains both of the letters o and h, or a and h, or o and a. They are sometimes also called the arcsin, arccos, and arctan. Step 1 the two sides we know are a djacent (6,750) and h ypotenuse (8,100). Choose which trig ratio to use. Cos a° = 6,750/8,100 = 0.8333. Sides in geometry, if you're given a right triangle with missing angles or sides, you can use trigonometric ratios—sine, cosine, or tangent—to find them. Adjacent, opposite and hypotenuse, in a right triangle is shown below. How do you find the missing angles of a right triangle? Using trig ratios to solve triangles: 🌎 brought to you by: To help you decide which of the three trigonometric ratios to use, you can label the sides of the triangle as adjacent or opposite. E) what if we now wanted to find the measure of the other acute angle of the triangle? 👉 learn how to find a missing angle of a right triangle.
Adjacent, opposite and hypotenuse, in a right triangle is shown below how to find missing angles in a triangle. Given a right angle triangle, the method for finding an unknown angle a, can be summarized in three steps :